The spleen is an organ located in the upper left portion of the abdomen just under the diaphragm. It mainly functions as a filter for the blood that flows through it, removing old or damaged blood cells from circulation. It also serves a role in the body’s immune function, helping the body identify and kill bacteria. In addition, it can act as a storage site for platelets and other blood cells.
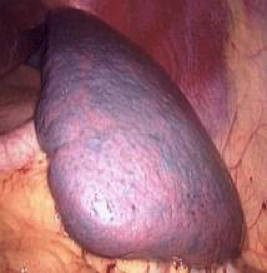
Who Needs The Spleen Removed?
There are several conditions which may require a splenectomy. Removal of the spleen is sometimes required if the platelet count is abnormally low. There are also various blood disorders that can cause the spleen to become abnormally enlarged or to act irregularly. Some conditions that may require splenectomy include
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Hemolytic anemia
- Sickle cell disease
- Hereditary spherocytosis
- Thalassemia major
- Certain types of lymphoma/leukemia
- Splenic infarct or aneurysm
Laparoscopic splenectomy is a technique of removing the spleen through several small incisions instead of the traditionally large, open incision. This technique has multiple advantages including reduced pain after surgery, less scarring, and a quicker return to normal activities. This technique can be utilized on most patients who require a splenectomy.
Aftercare and Recovery
Most people who have their spleens removed have no clinical side effects. Many of the functions of the spleen can be accomplished by other organs. There are certain bacterial infections that people are more susceptible to after a splenectomy. Preoperative vaccinations against the bacteria are normally administered to help decrease this incidence, and intermittent immunizations will be required postoperatively. This is particularly important in younger patients, and it is important to seek medical attention early if any infection develops.
The incidence of these bacterial infections overall is uncommon (less than 1%). The platelet count can also rise after splenectomy and should be monitored. Patients occasionally have to take aspirin products to help reduce the function of platelets.
Johns Creek Surgery, PC, located in Johns Creek, GA, attracts patients from all over the metro Atlanta area and beyond including Duluth, Alpharetta, Milton, Roswell, Gainesville, Canton, and Marietta, GA. Our board certified surgeons, Dr. Christopher Hart and Dr. William H. Johnson perform medical procedures or surgeries that do not require an overnight stay.
